CVS Uworld Q's
- Simple Medicine
- Feb 7, 2022
- 4 min read
Updated: May 3, 2022
Types of Shock:

Enlarged heart and pulmonary edema: Hight output HF (due to excessive flow through arteriovenous fistula): This type of fistula is surgically created to form an enlarged vein for hemodialysis. This causes too much blood flow which decreases SVR, essentially afterload. This then causes increase in venous return, essentially preload. And this of course causes an increase in SV, essentially Cardiac output.

Answer is therefore D.

Massive Pulmonary Embolism can lead to obstructive shock and hypotension.
How would this look in a question? Woman has shortness of breath and chest pain that occured an hour after physical work. Has jugular venous distension. What would be seen on echocardiography? Enlarged right ventricle: the PE increases RV pressure, causing enlargment.



Hypovolemic shock: Multiple lacerations and pelvic fracture indicate internal bleeding. How are these parameters affected?

Answer is E:

Intracellular Calcium regulation:

Which protein is responsible for the rapid decrease in cytoplasmic calcium level immediately preceding relaxation? Na/Ca2+ exchanger.
Initial calcium influx is detected by ryanodine receptors in SER, triggering further release of calcium into cytoplasm. Calcium from SER then binds to troponin C and tropomyosin is now moved out of the way for actin and myosin to bind. Intracellular calcium is removed by Na/Ca exchanger and SERCA (SER calcium ATPase pump).

Which antihypertensive drug causes color vision alterations, nausea and vommitting, confusion and anorexia? Digoxin

Other effects of ANP and BNP in response to atrial and ventricular wall stretch respectively? increase GFR, natriuresis and diuresis

Athelete's heart adaptations



How does milrinone cause vasodilation? It treats patients with refractory heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction. It inhibits PDE-3, so reduces degradation of cAMP. It causes calcium influx into myocytes to increase contractility and it also since calcium MLCK interaction is reduced, vasodilation occurs, which reduces cardiac preload and afterload.

Where should the ablation tip of the permanent ventricular pacemaker be placed? At the interatrial septum, near the opening of the coronary sinus
How are these parameters affected in a woman who is not pregnant compared to a pregnant one?

Fetal growth requires a lot of energy so causes an increase in metabolic demand for the mother to grow a healthy baby. This includes both heart and lung changes. The main thing to remember is that there is a decrease in systemic vascular resistance (allowing blood to return to the heart quicker, which increases preload aka cardiac venous return. Also reduces blood pressure so therefore afterload) and an increase in blood volume. This combination causes an increase in SV, which causes increase in Cardiac output as well.
The answer is E.
Like in Pregnancy, during Exercise, the body's metabolic demands have increased: Changes which occur to facilitate this are: increase in HR and Cardiac output to meet tissue O2 demands. Changes in Partial pressure of O2 and CO2 occur in the venous blood

In the first breaths of an infant, there is an increase in O2 tension in the lungs, causing a massive drop in pulmonary vascular resistance. Clamping of the umbilical cord, of course removes the low resistance placenta from circulation, causing SVR to increase. Answer: D

How does Phenylephrine affect these parameters? It's an alpha 1 agonist, so A is the answer.

Interventricular septal hypertrophy and increased LV mass. Patient started on beta blockers and symptoms improve. Why? It reduces LV contractility: Cardiac hypertrophy, causing decrease in LV blood volume. Beta blockers essentially remedy this by decreases contractility to allow more blood volume in LV.
How does cardiac hypertrophy occur? Addition of contractile myocardial fibers in response to chronic pressure overload of the ventricle. Common causes include aortic stenosis and long term hypertension.
How to alleviate LV outflow obstruction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? By increasing LV blood volume.
What maneuvers can increase LV blood volume? Passive leg elevation: increases preload. Hand grip: increases afterload.

What findings would you see on ECG of HCM?

Answer is D.
Systolic mumur that accenuates when standing from a supine position? Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
What worsens left ventricular outflow obstruction in HCM patients? A decrease in LV volume. This can be caused by vasodilators (which decrease SVR, leading to decreased afterload) and diuretics (which decrease LV venous filling (preload) and result in greater outflow obstruction)
Where should the ablation tip of a catheter be placed in the heart? Interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus.
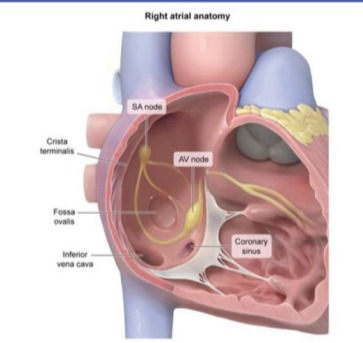
Link between dilated coronary sinus and pulmonary hypertension? Coronary sinus communicates freely with RA, so anything (like pulmonary hypertension) that causes increase in RA, will cause dilation of coronary sinus.
Why are LV gallops (S3 or S4) heard best at the end of expiration? The sound is more audible when the lung volume is decreased. This brings the heart (particularly the apex) closer to the chest wall.
How does a carotid massage help the patient's heart palpatations? By prolonging AV node refractory period. The whole point of a carotid massage is to slow down your heart rate. So how does it do that? It stimulates the baroreceptors on the carotid sinus, which increases afferent firing, which in turn increases vagal parasympathetic tone.
Orthopnea, pulmonary crackles and S3 heart sound, indicates decompensated heart failure. This is a common cause of secondary mitral regurgitation. The HF leads to increase in LV EDV (preload), with dilation of Mitral valve annulus and stretching of chordae tendinae. This causes insufficient closure of the valve, causing MR. Treated well with diuretics and vasodilators, since too much fluid is our main problem. If it were primary MR, this treatment would not have worked. The murmur intensity would not have decreased.
How does the Valsalva maneuver work? It decreases LV blood volume (preload). Abrupt standing does the same.
Mechanisms to increase preload? Squatting (increases SVR which forces a higher portion of RV output to enter the lungs and oxygenate blood to increase arterial oxygen concentration) or leg raising
What increases afterload? Handgrip (increases the pressure against which the heart has to pump).
Murmurs:
Systolic ejection murmur heard at left upper sternal border? ASD (pulmonic flow murmur): There is more blood flowing into the right atrium from the left atrium, so RV therefore has more blood to push through the pulmonic valve and is heard during systole (ejection). APT M: (refer auscultation diagram). Pulmonic sound is heard at left upper sternal border.
Holosystolic murmur best heard at left lower sternal border? VSD
Murmur is heard best when the patient sits up and leans forward? Aortic regurgitation. Loudest at point C :



Comments